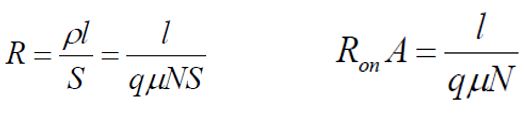***This article is intended for non-commercial research and private study.
Introduction
A semiconductor is a substance that possesses both the characteristics of a conductor, allowing electricity to flow, and an insulator, which restricts the flow of electricity. Among the devices that utilize semiconductors, those involved in controlling and converting electrical power, such as power supplies, are referred to as power semiconductors.
Power Semiconductor
A power semiconductor is a type of semiconductor device specifically designed to handle high power and high voltage levels. It is used in various applications where efficient control and conversion of electrical power are required. Power semiconductors play a crucial role in power electronics, which is the technology of converting and controlling electrical power.
Primary applications of power semiconductor
Power semiconductors are installed in all electronic devices with power circuits. They are utilized in our daily lives in devices such as smartphones, computers, televisions, air conditioners, and refrigerators. In the high-power field, they are widely used for power control in electric vehicles, trains, 5G base stations, industrial equipment, solar power generation, and other applications. 
Four functions of power semiconductor circuits 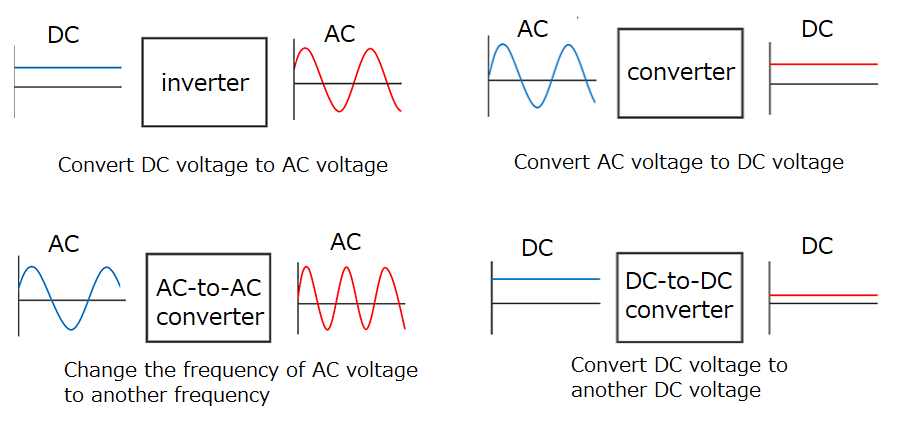
Some common types of power semiconductor and their operation
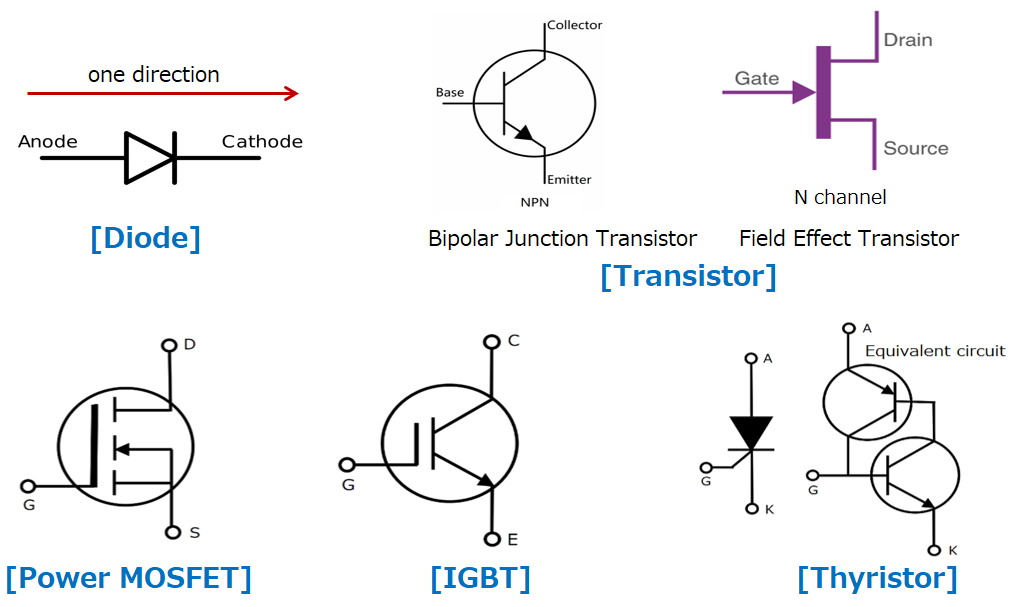
- Diode: A diode is two-terminal devices that allow current to flow in one direction and block it in the reverse direction. They are widely used in rectification circuits to convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC).
- Transistor: A transistor is three-terminal devices that can amplify or switch electrical signals and handle high power levels. They are used in applications such as motor control, power supplies, and audio amplifiers.
- Power MOSFET: A power MOSFET is a specific type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor(MOSFET) designed to handle significant power levels, it’s a type of power transistor that are known for their low on-resistance and fast switching speed. They are widely used in applications such as power supplies, DC-DC converters, and audio amplifiers.
- IGBT: An insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) is a type of power transistor that combines the high-speed switching capability of a transistor with the low on-resistance of a power MOSFET. They are commonly used in applications requiring high voltage and high current switching, such as in motor drives and power converters.
- Thyristor: A thyristor are four-layer, three-terminal semiconductor devices that can control large amounts of electrical power. They are commonly used in applications where the power needs to be controlled, such as in AC voltage regulators and motor speed control.
DRAM
The computer component called “memory” can be broadly divided into two types: “volatile” and “non-volatile”. Volatile memory, such as RAM (Random Access Memory), allows data to be stored only when electric current is flowing. It is primarily used as the main memory in computers and serves as a workspace for the operating system and applications to run. On the other hand, non-volatile memory refers to memory that can retain data even when the power is turned off, such as ROM (Read Only Memory) and flash memory. It is used as storage media for saving and recording data, such as SSDs and USB memory. NOR flash and NAND flash are two main types of flash memory.
DRAM(Dynamic Random Access Memory) is a type of computer memory that is used to store and access data temporarily while your computer is running. Think of DRAM as your computer’s short-term memorys, when you open a program or a file, the data is loaded into the DRAM for quick access by the processor, contributing to its overall speed and performance.
How it works: DRAM is made up of tiny memory cells, each of which can store a single bit of information, either a 0 or a 1. These cells are organized in a grid-like structure, forming a memory chip. When your computer needs to read or write data, it sends electrical signals to the appropriate memory cells.
DRAM needs to be constantly refreshed. This is because the electrical charge stored in each memory cell gradually leaks away over time. To prevent data loss, the computer regularly refreshes the charge in the cells, ensuring that the data remains intact. Another important aspects of DRAM is its capacity. It determines how much data your computer can store and access at any given time. More capacity means your computer can handle larger and more complex tasks.
However, DRAM is volatile, which means it loses all the stored data when the power is turned off. That’s why your computer needs a different type of memory, called a hard drive or solid-state drive, to store data permanently. DRAM is much faster than other types of storage like hard drives, which makes it ideal for tasks that require quick access to data, such as running programs or loading files.
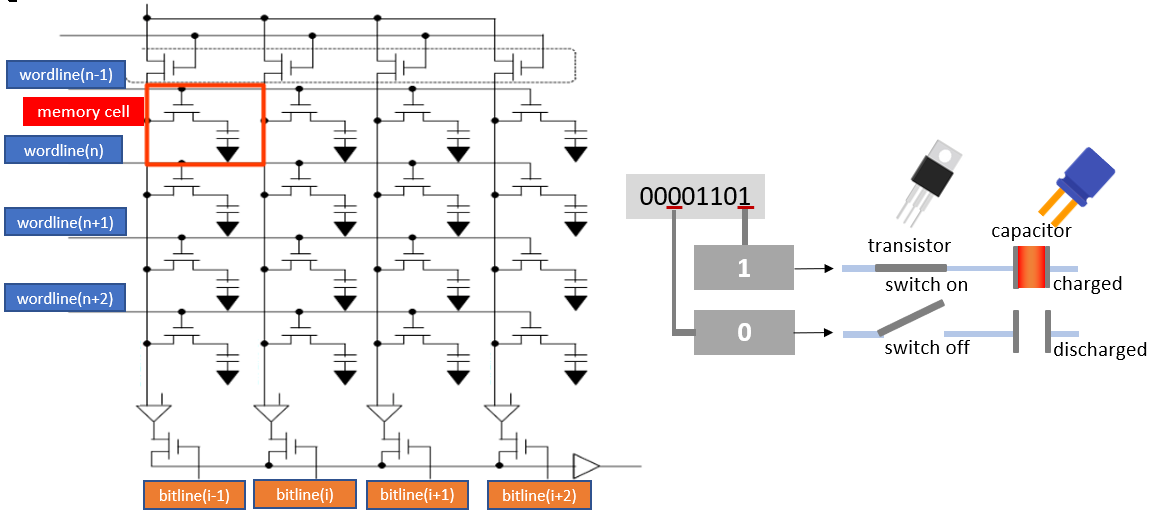 DRAM operation
DRAM operation 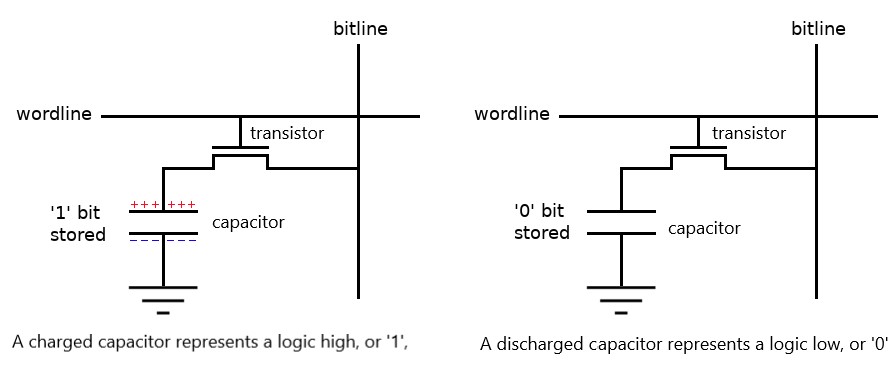 DRAM memory cell operation
DRAM memory cell operation
Basic Characteristics of Power Semiconductor
ON Resistance: The resistance value between the Drain and Source of a MOSFET during operation (ON) is called the ON Resistance (RDS(ON)). The smaller this value is, the lower the (power) loss.
In this context, ρ represents resistivity, q represents electronic charge, μ represents mobility, N represents impurity concentration, l represents length, and S represents area. From the euqation, if you want to reduce resistance, you can increase mobility,concentration, or make the current path shorter. Therefore, when discussing on-resistance, it is common to refer the on-resistance per unit area, RonA.
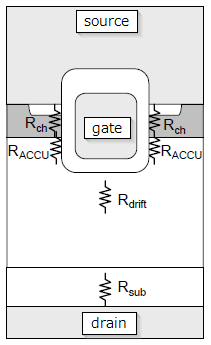 An Example of trench gate power MOSFET resistance
An Example of trench gate power MOSFET resistance
To be continued